WebAUGUSTUS Prediction Tutorial
This website explains step-by-step how to use the AUGUSTUS prediction web server application to predict genes in a genomic sequence. You find a similar tutorial on how to train AUGUSTUS parameters here (click).
Functionalities of the AUGUSTUS prediction web server application are (with a single run):
- Generation of hints (if a cDNA file is supplied)
- Prediction of genes in a genome sequence file using the supplied parameters. Genes will be predicted ab initio and with hints (the latter only if a cDNA and/or hint file is provided).
1 - Job submission in general
1.1 - Finding the prediction submission form
1.2 - Filling in general job data
1.2.1 - E-mail address
1.2.2 - AUGUSTUS species parameters
1.2.2.1 - Uploading an archive file
1.2.2.2 - Project identifier
1.2.3 - Genome file
1.2.3.1 - Genome file format
1.2.3.2 - Genome file upload options
1.2.3.3 - What the genome file is used for
1.3 - Optional fields
1.3.1 - cDNA file
1.3.1.1 - cDNA file format
1.3.1.2 - cDNA file upload options
1.3.1.3 - What cDNA files are used for
1.3.2 - Hints file
1.3.1.1 - Hints file format
1.3.1.2 - What hints files are used for
1.3.3 - UTR prediction
1.3.4 - Strand specific prediction
1.3.5 - Alternative transcripts
1.3.6 - Allowed gene structure
1.4 - Verification that you are a human
1.5 - The submit button
1.6 - Example data files
2 - What happens after submission
2.1 - Submission duplication
2.2 - Errors during prediction
3 - Prediction Results
The pipeline invoked by submitting a job to the AUGUSTUS prediction web server application is straight forward. If a cDNA file is supplied, hints are first generated from this cDNA file. If no cDNA file is supplied, AUGUSTUS is immediately called with the specified parameters.
The input fields of the AUGUSTUS prediction web server application form are: E-mail, AUGUSTUS species parameters, Genome file, cDNA file, Hints file and a number of options in form of checkboxes.
Please be aware that the submission of cDNA files will invoke the software BLAT [2], which is on our server available for academic, personal and non-profit use, only.
In the following, you find detailed instructions for submitting an AUGUSTUS prediction job.
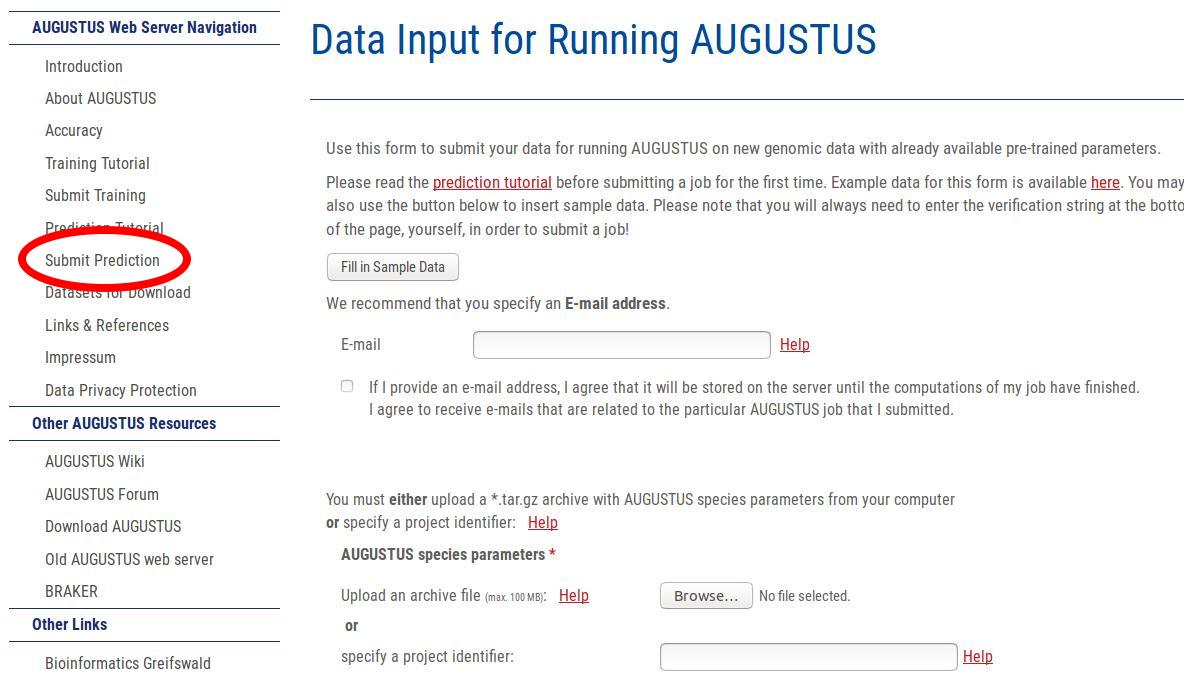
You find the WebAUGUSTUS prediction submission form by clicking on the following link in the left side navigation bar:
 |
This section describes all fields that should be filled in for every job submission, i.e. fields that are obligatory (except for the email address, which is optional but strongly recommended).
At first, we recommend that you enter a valid e-mail address:
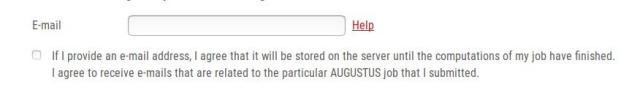 |
It is possible to run WebAUGUSTUS without giving an e-mail address but here are some reasons why we recommend supplying an e-mail address:
- Unlike many other bioinformatics web services, the AUGUSTUS web server application is not an implementation of a fail-safe procedure. Our pipeline may issue warnings or errors, and sometimes, we need to get some feedback from you via e-mail in order to figure out what is the problem with your particular input data set.
- In addition, running AUGUSTUS on large files is rather time consuming process that may take up to several weeks (depending on the input data). It may be more convenient to receive an e-mail notification about your job having finished, than checking the status page over and over, again
We use your e-mail address for the following purposes:
- Confirming your job submission
- Confirming successful file upload (for large files via ftp/http link)
- Notifying you that your job has finished
- Informing you about any problems that might occur during your particular AUGUSTUS prediction job
We do not use your e-mail address to send you any spam, i.e. about web service updates. We do not share your e-mail address with any third parties. Please read our Data Privacy Protection declaration.
Job submission without giving an email address is possible but discouraged for large input files.
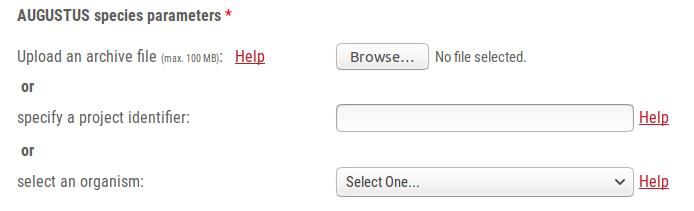
The web server application offers you three options to specify which parameter set you want to use for predicting genes with AUGUSTUS. You can either uploaded a *.tar.gz parameter archive from your local harddrive, or you can specify the job ID of a previously finished AUGUSTUS web server application training run, or you can select a pre-trained parameter set through the drop-down menu.
 |
A *.tar.gz archive with a folder containing the following files is required for predicting genes in a new genome with pre-trained parameters:
- species/species_parameters.cfg
- species/species_metapars.cfg
- species/species_metapars.utr.cfg
- species/species_exon_probs.pbl.withoutCRF
- species/species_exon_probs.pbl
- species/species_weightmatrix.txt
- species/species_intron_probs.pbl
- species/species_intron_probs.pbl.withoutCRF
- species/species_igenic_probs.pbl
- species/species_igenic_probs.pbl.withoutCRF
where species is replaced by the name of the species you trained AUGUSTUS for (e.g. carrot would result it carrot/carrot_parameters.cfg). The additional species before the slash means that all those files must reside in a directory that is called species before you tar and gzip it. If you simply tar and gzip the folder that contains parameters of an AUGUSTUS training run, everything should work fine.
If you trained AUGUSTUS on this webserver, you may instead of downloading and re-uploading a parameter archive, simply specify the project identifier of this training run. You find the project identifier for example in the job confirmation e-mail. It starts either with train or with pred and is followed by 8 digits.
In addition to using parameters that you trained yourself, you may also use pre-trained parameters for the following species:
| Species | Project identifier | Courtesy of |
| Animals | ||
| Acyrthosiphon pisum | pea_aphid | |
| Aedes aegypti | aedes | |
| Amphimedon queenslandica | amphimedon | |
| Apis dorsata | adorsata | Francisco Camara Ferreira |
| Apis mellifera | honeybee1 | Katharina Hoff and Mario Stanke |
| Bombus terrestris | bombus_terrestris2 | Katharina Hoff |
| Brugia malayi | brugia | |
| Caenorhabditis elegans | caenorhabditis | |
| Callorhinchus milli | elephant_shark | Tereza Manousaki and Shigehiro Kuraku |
| Camponotus floridanus | camponotus_floridanus | Shishir K Gupta |
| Danio rerio | zebrafish | |
| Drosophila melanogaster | fly | |
| Heliconius melpomene | heliconius_melpomene1 | Sebastian Adler and Katharina Hoff |
| Gallus gallus domesticus | chicken | Stefanie König |
| Homo sapiens | human | |
| Nasonia vitripennis | nasonia | |
| Petromyzon marinus | sealamprey | Falk Hildebrand and Shigehiro Kuraku |
| Schistosoma mansoni | schistosoma | |
| Tribolium castaneum | tribolium | |
| Trichinella spiralis | trichinella | |
| Alveolata | ||
| Tetrahymena thermophila | tetrahymena | |
| Toxoplasma gondii | toxoplasma | |
| Protozoa | ||
| Leishmania tarantolae | leishmania_tarentolae | |
| Plants and algae | ||
| Arabidopsis thaliana | arabidopsis | |
| Chlamydomonas reinhartii | chlamy2011 | |
| Galdieria sulphuraria | galdieria | |
| Triticum aestivum | wheat | Stefanie König |
| Zea mays | maize | |
| Solanum lycopersicum | tomato | |
| Fungi | ||
| Aspergillus fumigatus | aspergillus_fumigatus | Jason Stajich |
| Aspergillus nidulans | aspergillus_nidulans | Jason Stajich |
| Aspergillus oryzae | aspergillus_oryzae | Jason Stajich |
| Aspergillus terreus | aspergillus_terreus | Jason Stajich |
| Botrytis cinerea | botrytis_cinerea | Jason Stajich |
| Candida albicans | candida_albicans | Jason Stajich |
| Candida guilliermondii | candida_guilliermondii | Jason Stajich |
| Candida tropicalis | candida_tropicalis | Jason Stajich |
| Chaetomium globosum | chaetomium_globosum | Jason Stajich |
| Coccidioides immitis | coccidioides_immitis | Jason Stajich |
| Coprinus cinereus | coprinus | Jason Stajich |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | cryptococcus_neoformans_neoformans_B | Jason Stajich |
| Debaryomyces hansenii | debaryomyces_hansenii | Jason Stajich |
| Encephalitozoon cuniculi | encephalitozoon_cuniculi_GB | Jason Stajich |
| Eremothecium gossypii | eremothecium_gossypii | Jason Stajich |
| Fusarium graminearum | fusarium_graminearum | Jason Stajich |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | histoplasma_capsulatum | Jason Stajich |
| Kluyveromyces lactis | kluyveromyces_lactis | Jason Stajich |
| Laccaria bicolor | laccaria_bicolor | Jason Stajich |
| Lodderomyces elongisporus | lodderomyces_elongisporus | Jason Stajich |
| Magnaporthe grisea | magnaporthe_grisea | Jason Stajich |
| Neurospora crassa | neurospora_crassa | Jason Stajich |
| Phanerochaete chrysosporium | phanerochaete_chrysosporium | Jason Stajich |
| Pichia stipitis | pichia_stipitis | Jason Stajich |
| Phizopus oryzae | rhizopus_oryzae | Jason Stajich |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | saccharomyces_cerevisiae_S288C | Jason Stajich |
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | schizosaccharomyces_pombe | Jason Stajich |
| Ustilago maydis | ustilago_maydis | Jason Stajich |
| Verticillium longisporum | verticillium_longisporum1 | Katharina Hoff and Mario Stanke |
| Yarrowia lipolytica | yarrowia_lipolytica | Jason Stajich, modified by Katharina Hoff |
| Archaea (experimental parameters) | ||
| Sulfolobus solfataricus | sulfolobus_solfataricus | Katharina Hoff |
| Bacteria (experimental parameters) | ||
| Escherichia coli | E_coli_K12 | Katharina Hoff |
| Thermoanaerobacter tencongensis | thermoanaerobacter_tengcongensis | Katharina Hoff |
Please let us know whether you want to have parameters that you trained for a certain species to be included in this public list! If they are included in this list, they will also be distributed with the upcoming AUGUSTUS release.
The genome file is an obligatory input for predicting genes with AUGUSTUS.
The genome file must contain the genome sequence in (multiple) fasta format. Every unique header begins with a >. The sequence must be DNA. Allowed sequence characters: A a T t G g C c H h X x R r Y y W w S s M m K k B b V v D d N n. (Internally, AUGUSTUS will interpret everything that is not A a T t C c G g as an N!) Empty lines are not allowed. If they occur, they will automatically be removed by the webserver application. White spaces in the sequence header might cause problems if the first word after the leading character > is identical for several fasta entries. We generally recommend short, unique, non-white-space containing fasta headers.WebAUGUSTUS does have a strict limit for character per line for FASTA format files. Disobeying this restriction might cause memory issues on our server. We recommend to format sequences in FASTA files submitted to WebAUGUSTUS with a unix linebreak after 80 characters.
Correct file format example:
>Chr.1
CCTCCTCCTGTTTTTCCCTCAATACAACCTCATTGGATTATTCAATTCAC
CATCCTGCCCTTGTTCCTTCCATTATACAGCTGTCTTTGCCCTCTCCTTC
TCTCGCTGGACTGTTCACCAACTCTCAGCCCGCGATCCCAATTTCCAGAC
AACCCATCTTATCAGCTTGGCCACGGCCTCGACCCGAACAGACCGGCGTC
CAGCGAGAAGAGCGTCGCCTCGACGCCTCTGCTTGACCGCACCTTGATGC
TCAAGACTTATCGCGATGCCAAGAAGCGTCTCATCATGTTCGACTACGA
>Chr.2
CGAAACGGGCACCTATACAACGATTGAAACCATTATTCAAGCTCAGCAAG
CGTCTATGCTAGCGGTTATTGCGAGCACTTCAGCGGTTGCTACTACGACT
ACTACTTGATAAATGAAACGGCTATAAAAGAGGCTGGGGCAAAAGTATGT
TAGTTGAAGGGTGACCTGAACGATGAATCGGTCGAATTTTTTATTGGCAG
AGGGAAGGTAGGTTTACTCAATTTAGTTACTTCTAGCCGTTGATTGGAGG
AGCGCAAGCGACGAGGAGGCTCATCGGCCGCCCGCGGAAAGCGTAGTCT
TACACGGAAATCAACGGCGGTGTCATAAGCGAG
>Chr.3
.....
|
The maximal number of scaffolds allowed in a genome file is 250000. If your file contains more scaffolds, please remove all short scaffolds. For training AUGUSTUS, short scaffolds are worthless because no complete training genes can be generated from them. In terms of prediction, it is possible to predict genes in short scaffolds. However, those genes will in most cases be incomplete and probably unreliable.
Besides plain fasta format, our server accepts gzipped-fasta format for genome file upload. You find more information about gzip at the gzip homepage. Gzipped files have the file ending *.gz.
The AUGUSTUS prediction web server application offers two possiblities for transferring the genome file to the server: Upload a file and specify a web link to file.
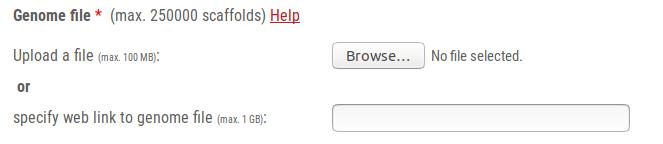 |
- For small files, please click on the Choose File or Browse-button and select a file on your harddrive.
If you experience a Connection timeout (because your file was too large for this type of upload - the size is browser dependent), please use the option for large files! - Large files can be retrieved from a public web link. Deposit your sequence file at a http or ftp server and specify the valid URL to your sequence file in the training submission form. Our server will fetch the file from the given address upon job submission. (File size limit: currently 1 GB. Please contact us in case you want to upload a bigger genome file, links to dropbox are not supported by WebAUGUSTUS.) You will be notified by e-mail when the file upload from web-link is finished (i.e. you can delete the file from the public server after you received that e-mail).
You cannot do both at the same time! You must either select a file on your harddrive or give a web link!
The genome file is used as a template for gene prediction, it is the sequence in which you want to predict genes.
This section describes a number of fields that are optional for predicting genes with AUGUSTUS.
This feature is available only for academic, personal and non-profit use as this is required by the BLAT license.
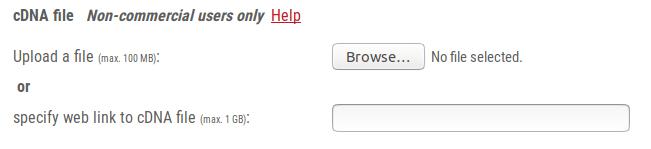 |
The cDNA file is a multiple fasta DNA file that contains e.g. ESTs or full-length cDNA sequences. Allowed sequence characters: A a T t G g C c H h X x R r Y y W w S s M m K k B b V v D d N n U u. Empty lines are not allowed and will be removed from the submitted file by the webserver application. An example for correct cDNA file format is given at 1.2.3.1 - Genome file format.
It is currently possible to submit assembled RNA-seq transcripts instead of or mixed with ESTs as a cDNA/EST file. However, you should be aware that RNA-seq files are often much bigger than EST or cDNA files, which increases runtime of a prediction job. In order to keep runtime of your prediction job as low as possible, you should remove all assembled RNA-seq transcripts from your file that do not map to the submitted genome sequence. (In principle, this holds true for EST and cDNA files, too, but there, the problem is not as pronounced due to a smaller number of sequences.)
It is currently not allowed to upload RNA-seq raw sequences. (We filter for the average length of cDNA fasta entries and may reject the entire training job in case the sequences are on average too short, i.e. shorter than 400 bp.)
Besides plain fasta format, our server accepts gzipped-fasta format for cDNA file upload. You find more information about gzip at the gzip homepage. Gzipped files have the file ending *.gz. The maximal supported file size is 1 GB.
There are two options for cDNA file upload: upload from your local harddrive, or upload from a public http or ftp server. Please see 1.2.3.2 - Genome file upload options for a more detailed description of upload options.
The cDNA file is used for generating extrinsic evidence for gene structures in the gene prediction process, also called hints
 |
It is possible to submit an externally created file that contains extrinsic evidence for gene structures in gff format.
Comment lines are not allowed.
It makes no sense to upload gene prediction files (e.g. augustus.gff from AUGUSTUS gene prediction) as hints to WebAUGUSTUS. This is therefore not allowed.
In general, gff files must contain the following columns (the columns are separated by tabulators):
- The sequence names must be found in the fasta headers of sequences in the genome file.
- The source tells with which software/process the gene structure was generated (you can fill in whatever you like).
-
The feature may for AUGUSTUS gene prediction be
- start - translation start, specifies an interval that contains the start codon. The interval can be larger than 3 nucleotides, in which case every ATG in the interval gets a bonus.
- stop - translation end (stop codon)
- tss - transcription start site
- tts - transcription termination site
- ass - acceptor (3') splice site, the last intron position
- dss - donor (5') splice site, the first intron position
- exonpart - part of an exon in the biological sense.
- exon - complete exon in the biological sense.
- intronpart - introns both between coding and non-coding exons.
- intron - complete intron in the biological sense
- CDSpart - part of the coding part of an exon. (CDS = coding sequence)
- CDS - coding part of an exon with exact boundaries. For internal exons of a multi exon gene this is identical to the biological boundaries of the exon. For the first and the last coding exon the boundaries are the boundaries of the coding sequence (start, stop).
- UTRpart - The hint interval must be included in the UTR part of an exon.
- UTR - exact boundaries of a UTR exon or the untranslated part of a partially coding exon.
- irpart - intergenic region part. The bonus applies to every base of the intergenic region. If UTR prediction is turned on (--UTR=on) then UTR is considered genic.
- nonexonpart - intergenic region or intron.
- genicpart - everything that is not intergenic region, i.e. intron or exon or UTR if applicable.
- Start is the beginning position of the line's feature, counting the first position of a sequence as position 1.
- Stop position, must be at least as large as start position.
- The score must be a number but the number is irrelevant to our web server applications.
- The strand denotes whether the gene is located on the forward (+) or on the reverse (-) strand.
- Frame is the reading frame, can be denoted as '.' if unknown or irrelevant. For exonpart and exon this is as defined as follows: On the forward strand it is the number of bases after (begin position 1) until the next codon boundary comes (0, 1 or 2). On the reverse strand it is the number of bases before (end position + 1) the next codon boundary comes (0, 1 or 2).
- For usage as hint, Attribute must contain the string source=M (for manual). Other sources, such EST or protein, are possible, but only in the command line version of AUGUSTUS. Source types other than M are ignored by AUGUSTUS web server applications.
Correct format example:
Chr.1 anchor exonpart 500 506 0 - . source=M
Chr.1 anchor exon 966 1017 0 + 0 source=M
Chr.1 anchor start 966 968 0 + 0 source=M
Chr.1 anchor dss 2199 2199 0 + . source=M
Chr.1 anchor stop 7631 7633 0 + 0 source=M
Chr.1 anchor intronpart 7631 7633 0 + 0 source=M
|
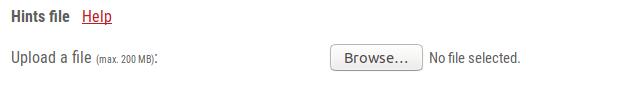
The hints file is used as extrinsic evidence that supports gene structure prediction. You can generate hints yourself based on any alignment program and information resource (e.g. ESTs, RNA-seq data, peptides, proteins, ...) that appears suitable to you.
 |
It takes significantly more time to predict UTRs but in addition to reporting UTRs, it usually is also a little more accurate on the coding regions when ESTs are given as extrinsic evidence.
UTR prediction is only possible if UTR parameter files exist for your species. Even if UTR parameter files exist for a species, you should make sure, that they are species specific, i.e. have actually been optimized for your target species. It is a waste of time to predict UTRs with general (template) parameters.
If no UTR parameter files exist for your species but you enables UTR prediction in the form, the web server application will overrule the choice to predict UTRs by simply not predicting any UTRs.
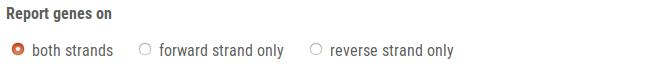 |
By default, AUGUSTUS predicts genes in both strands but you may alter this behavior by checking another radio button in this field to predict genes in the forward (+) or reverse (-) strand, only.
 |
By default, AUGUSTUS does not predict any alternative transcripts.
If you select few, then the following AUGUSTUS parameters are set to result in the prediction of relatively few alternative transcripts:
--alternatives-from-sampling=true --minexonintronprob=0.2 --minmeanexonintronprob=0.5
--maxtracks=2.
If you select medium the AUGUSTUS parameters are set to
--alternatives-from-sampling=true --minexonintronprob=0.08 --minmeanexonintronprob=0.4
--maxtracks=3".
If you select many, AUGUSTUS parameters are set to
--alternatives-from-sampling=true --minexonintronprob=0.08 --minmeanexonintronprob=0.3
--maxtracks=20".
 |
Predict any number of (possibly partial) genes: This option is set by default. AUGUSTUS may predict no gene at all, one or more genes. The genes at the boundaries of the input sequence may be partial. Partial here means that not all of the exons of a gene are contained in the input sequence, but it is assumed that the sequence starts or ends in a non-coding region.
Predict only complete genes: AUGUSTUS assumes that the input sequence does not start or end within a gene. Zero or more complete genes are predicted.
Predict only complete genes - at least one: As the previous option. But AUGUSTUS predicts at least one gene (if possible).
Predict exactly one complete gene: AUGUSTUS assumes that the sequence contains exactly one complete gene. Note: This feature does not work properly in combination with alternative transcripts.
Ignore conflicts with other strand: By default AUGUSTUS assumes that no genes - even on opposite strands - overlap. Indeed, this usually is the case but sometimes an intron contains a gene on the opposite strand. In this case, or when AUGUSTUS makes a false prediction on the one strand because it falsely thinks there is a conflicting gene on the other strand, AUGUSTUS should be run with this option set. It then predicts the genes on each strand separately and independently. This may lead to more false positive predictions, though.
 |
Trying to avoid abuse of our web server application through bots, we implemented a captcha. The captcha is an image that contains a string. You have to type the string from the image into the field next to the image.
 |
After filling out the appropriate fields in the submission form, you have to click on the button that says "Start Predicting" at the bottom of the page. It might take a while until you are redirected to the status page of your job. The reason is that we are checking various file formats prior job acceptance, and that the transfer of files from your local harddrive to our server might take a while. Please be patient and wait until you are redirected to the status page! Do not click the button more than once (it won't do any harm but it also doesn't speed up anything).
In the following, we provide some correctly formatted, compatible example data files:
http://bioinf.uni-greifswald.de/webaugustus/examples/honeybee1.tar.gz - This file is an example of a AUGUSTUS species parameter archive file. Please do not upload this archive to our server since the identical parameters are usable through the AUGUSTUS species parameter project identifier honeybee1 and a re-upload would simply duplicate this data set. We only provide this file as an example which may help you check your own parameter archive in case incompatibilities with your application might occur. These parameters were optimized for predicting genes in Apis mellifera.
http://bioinf.uni-greifswald.de/webaugustus/examples/LG16.fa - This file may be used as a Genome file. It contains linkage group 16 of Apis mellifera from GenBank (modified headers).
http://bioinf.uni-greifswald.de/webaugustus/examples/honeybee-ests.fa - This file may be used as a cDNA file. It contains 3 ESTs of Apis mellifera from GenBank (modified headers).
http://bioinf.uni-greifswald.de/webaugustus/examples/honeybee.hints - This file may be used as a Hints file. It contains hints that were generated from Apis mellifera RNA-Seq data for genome file LG16.fa.
You can insert some of these sample data sets by pressing the "Fill in Sample Data" button:
 |
After you click the "Start Predicting" button, the web server application first validates whether the combination of your input fields is generally correct. If you submitted an unsupported input combination you will be redirected to the training submission form and an error message will be displayed at the top of the page.
If all fields were filled in correctly, the application is actually initiated. You will receive an e-mail that confirms your job submission and that contains a link to the job status page (if you supplied an e-mail address). You will be redirected to the job status page.
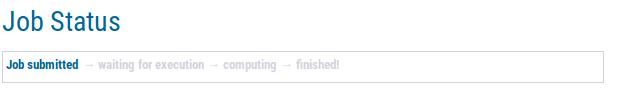 |
In the beginning, the status page will display that your job has been submitted. This means, the web server application is currently uploading your files and validating file formats. After a while, the status will change to waiting for execution. This means that all file formats have been confirmed and an actually AUGUSTUS training job has been submitted to our grid engine, but the job is still pending in the queue. Depending on waiting queue length, this status may persist for a while. Please contact us in case you job is pending for more than one month. Later, the job status will change to computing. This means the job is currently computing. When the page displays finished, all computations have been finished and a website with your job's results has been generated.
You will receive an e-mail when your job has finished (if you supplied an e-mail address).
Since predicting genes wiht AUGUSTUS may under certain circumstances be is a very resource consuming process, we try to avoid data duplication. In case you or somebody else tries to submit exactly the same input file combination more than once, the duplicated job will be stopped and the submitter of the redundant job will receive information where the status page of the previously submitted job is located.
You should automatically receive an e-mail in case an error occurs during the AUGUSTUS gene prediction process. The admin of this server is also notified by e-mail about errors. Please contact augustus-web@uni-greifswald.de if you want to find out what went wrong.
After job computations have finished, you will receive an e-mail (if you supplied an e-mail address). The job status web page may at this point in time look similar to this:
 |
This page should contain the file predictions.tar.gz. Please make a "right click" on the link and select "Save As" (or similar) to save the file on your local harddrive.
predictions.tar.gz is a gene prediction archive and its content depends on the input file combination. You can unpack the archive by typing tar -xzvf *.tar.gz into your shell. (You find more information about the software tar at the GNU tar website.)
Files that are always contained in gene prediction archives:
- *.gff - gene predictions in gff format
Format example AUGUSTUS prediction gff file:
# This output was generated with AUGUSTUS (version 2.6). # AUGUSTUS is a gene prediction tool for eukaryotes written by Mario Stanke (mario.stanke@uni-greifswald.de) # and Oliver Keller (keller@cs.uni-goettingen.de). # Please cite: Mario Stanke, Mark Diekhans, Robert Baertsch, David Haussler (2008), # Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding # Bioinformatics 24: 637-644, doi 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn013 # reading in the file /var/tmp/augustus/AUG-1855139717/hints.gff ... # Setting 1group1gene for E. # Sources of extrinsic information: M E # Have extrinsic information about 1 sequences (in the specified range). # Initializing the parameters ... # human version. Use default transition matrix. # Looks like /var/tmp/augustus/AUG-1855139717/input.fa is in fasta format. # We have hints for 1 sequence and for 1 of the sequences in the input set. # # ----- prediction on sequence number 1 (length = 6483, name = Chr.1) ----- # # Delete group HintGroup , 5803-5803, mult= 1, priority= -1 1 features # Forced unstranded hint group to the only possible strand for 3 groups. # Deleted 1 groups because some hint was not satisfiable. # Constraints/Hints: Chr.1 anchor start 182 184 0 + . src=M Chr.1 anchor stop 3058 3060 0 + . src=M Chr.1 anchor dss 4211 4211 0 + . src=M Chr.1 b2h ep 1701 2075 0 . . grp=154723761;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h ep 1716 2300 0 + . grp=13907559;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h ep 1908 2300 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h ep 3592 3593 0 + . grp=13907559;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h ep 3836 3940 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h ep 5326 5499 0 + . grp=27937842;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h ep 5805 6157 0 + . grp=27937842;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h exon 3142 3224 0 + . grp=13907559;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h exon 3142 3224 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h exon 3592 3748 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 anchor intronpart 5000 5100 0 + . src=M Chr.1 b2h intron 2301 3141 0 + . grp=13907559;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h intron 2301 3141 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h intron 3225 3591 0 + . grp=13907559;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h intron 3225 3591 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h intron 3749 3835 0 + . grp=154736078;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 b2h intron 5500 5804 0 + . grp=27937842;pri=4;src=E Chr.1 anchor CDS 6194 6316 0 - 0 src=M Chr.1 anchor CDSpart 5900 6000 0 + . src=M # Predicted genes for sequence number 1 on both strands # start gene g1 Chr.1 AUGUSTUS gene 182 3060 0.63 + . g1 Chr.1 AUGUSTUS transcript 182 3060 0.63 + . g1.t1 Chr.1 AUGUSTUS start_codon 182 184 . + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS initial 182 225 1 + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS internal 1691 2300 0.86 + 1 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS terminal 3049 3060 0.74 + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS CDS 182 225 1 + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS CDS 1691 2300 0.86 + 1 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS CDS 3049 3060 0.74 + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; Chr.1 AUGUSTUS stop_codon 3058 3060 . + 0 transcript_id "g1.t1"; gene_id "g1"; # coding sequence = [atgatgaaaccctgtctctaccaaaaagacaaaaaattagccagctcaagcaagcactactcttcctcccgcagtggag # gaggaggaggaggaggaggatgtggaggaggaggaggagtgtcatccctaagaatttctagcagcaaaggctcccttggtggaggatttagctcaggg # gggttcagtggtggctcttttagccgtgggagctctggtgggggatgctttgggggctcatcaggtggctatggaggattaggaggttttggtggagg # tagctttcatggaagctatggaagtagcagctttggtgggagttatggaggcagctttggagggggcaatttcggaggtggcagctttggtgggggca # gctttggtggaggcggctttggtggaggcggctttggaggaggctttggtggtggatttggaggagatggtggccttctctctggaaatgaaaaagta # accatgcagaatctgaatgaccgcctggcttcctacttggacaaagttcgggctctggaagaatcaaactatgagctggaaggcaaaatcaaggagtg # gtatgaaaagcatggcaactcacatcagggggagcctcgtgactacagcaaatactacaaaaccatcgatgaccttaaaaatcagagaacaacataa] # protein sequence = [MMKPCLYQKDKKLASSSKHYSSSRSGGGGGGGGCGGGGGVSSLRISSSKGSLGGGFSSGGFSGGSFSRGSSGGGCFGG # SSGGYGGLGGFGGGSFHGSYGSSSFGGSYGGSFGGGNFGGGSFGGGSFGGGGFGGGGFGGGFGGGFGGDGGLLSGNEKVTMQNLNDRLASYLDKVRAL # EESNYELEGKIKEWYEKHGNSHQGEPRDYSKYYKTIDDLKNQRTT] # Evidence for and against this transcript: # % of transcript supported by hints (any source): 20 # CDS exons: 1/3 # E: 1 # CDS introns: 0/2 # 5'UTR exons and introns: 0/0 # 3'UTR exons and introns: 0/0 # hint groups fully obeyed: 0 # incompatible hint groups: 5 # E: 3 (gi|154723761,gi|13907559,gi|154736078) # M: 2 # end gene g1 ###
Different kinds of information are printed after the hash signs, e.g. the applied AUGUSTUS version and parameter set, predicted coding sequence and amino acid sequence. Predictions and hints are given in tabulator separated gff format, i.e. the first column contains the target sequence, second column contains the source of the feature, third column contains the feature, forth column contains the feature start, fifth column contains the feature end, sixth column contains a score (if applicable), seventh column contains the strand, eightth column contains the reading frame and nineth column contains either for hints the grouping and source information, or for prediction lines the gene/transcript identifier.
Files that may optionally be contained in gene prediction archives:
- *.gtf - gene predictions in gtf format
- *.aa - gene predictions as protein fasta sequences
- *.codingseq - gene predictions as CDS DNA fasta sequences
- *.cdsexons - predicted exons in DNA fasta sequences
- *.mrna - predicted mRNA sequences (with UTRs) in DNA fasta sequences
- *.gbrowse - gene prediction track for the GBrowse genome browser
Click here to view a real AUGUSTUS prediction web service output!
It is important that you check the results of an AUGUSTUS gene prediction run. Do not trust predictions blindly! Prediction accuracy depends on the input sequence quality, on hints quality and on whether a given parameter set fits to the species of the supplied genomic sequence.
Results of your job are deleted from our server after 180 days.
