About AUGUSTUS
AUGUSTUS is a program that predicts genes in eukaryotic genomic sequences. It can be run with pre-trained parameters on this web server or be downloaded and run locally. It is open source so you can compile it for your computing platform. You can also run AUGUSTUS on the German MediGRID. This enables you to submit larger sequence files and allows to use protein homology information in the prediction. The MediGRID requires an instant easy registration by email for first-time users.
The AUGUSTUS training web server application automatically generates training gene sets from genomic sequence(s) and a set of Proteins or ESTs and subsequently trains AUGUSTUS parameters for a new species, and runs gene predictions with the new parameters and the supplied extrinsic evidence. Alternatively, you can also download the autoAug.pl pipeline and execute our training and prediction pipeline locally.
Features
Gene prediction with AUGUSTUS
- AUGUSTUS now has a protein profile extension (PPX) which allows to use protein family specific conservation in order to identify members and their exon-intron structure of a protein family given by a block profile. The block profile can be constructed with accompanying scripts from a multiple protein sequence alignment. For more details please refer to the README.md.
- The download version of AUGUSTUS can incorporate data from RNA-Seq (short cDNA reads, single or paired-end, e.g. from Illumina or SOLiD) as documented here (January 8, 2012).
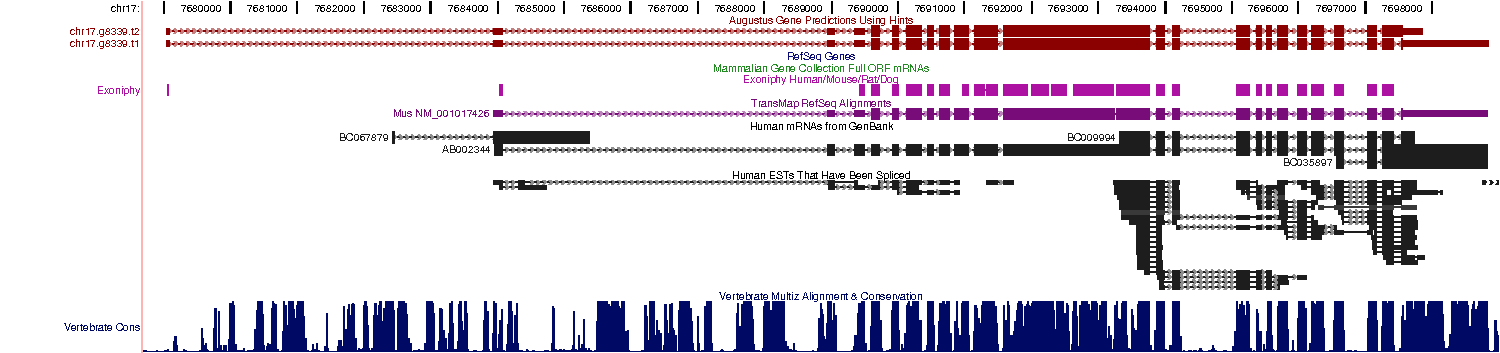
- If you use the old AUGUSTUS web server application, the results can be displayed automatically in the genome browser Gbrowse. You can browse the gene predictions together with the input sequence, the constraints and the cDNA alignments. Gbrowse also enables you to simultaneously display your own annotation and to export the image in scalable vector graphics format
- You can upload cDNA sequences together with the genomic DNA. Your ESTs or mRNA will be used to improve the gene prediction.
- AUGUSTUS usually belongs to the most accurate programs for the species it is trained for. Often it is the most accurate ab initio program. For example, at the independent gene finder assessment (EGASP) on the human ENCODE regions AUGUSTUS was the most accurate gene finder among the tested ab initio programs. At the more recent nGASP (worm), it was among the best in the ab initio and transcript-based categories. See accuracy statistics for further statics.
-
AUGUSTUS can be used ab initio and has a flexible mechanism for incorporating extrinsic
information, e.g. from EST alignments and protein alignments. Here is an example from the UCSC
Genome Browser where the AUGUSTUS prediction incorporates mRNA alignments, EST alignments,
conservation and other sources of information:
-
AUGUSTUS can predict alternative splicing and alternative transcripts. It can do this for example
when the EST alignments suggest alternative splicing like in this example:
- AUGUSTUS can predict the 5'UTR and 3'UTR including introns. This is in particular helpful when using EST alignments as the majority of ESTs aligns in the untranslated regions (example). This feature is currently only trained for human, the red algae Galdieria sulphuraria, Caenorhabditis elegans, Toxoplasma gondii, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, pea aphid, Culex pipens (3'UTR only), butterfly, Bombus terrestris/impatiens, chlorella, elephant shark, honeybee, Leishmania tarentolae, maize, rhodius, tomato, trichinella.
- AUGUSTUS can report a large number of alternative genes, including probabilities for the transcripts and each exon and intron. You can make AUGUSTUS predict suboptimal gene structures (example) and you can adjust command line parameters to regulate the number of reported alternatives.
Training AUGUSTUS
- AUGUSTUS is retrainable. It comes with a training program that estimates the parameters given a training set of known genes. It also comes with an optimization script that tries to find values for the meta parameters, like splice window sizes, that optimize the prediction accuracy. The training program is also available through a web interface.
Parameters are already available for the following species:
AUGUSTUS has currently been trained on species specific training sets to predict genes in the following species. Note that for closely related species usually only one version is necessary. For example, the human version is good for all mammals. Contributions.
| animals: | alveolata: | plants and algae: | fungi: |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Acyrthosiphon pisum Aedes aegypti Amphimedon queenslandica Apis mellifera Brugia malayi Caenorhabditis elegans Callorhinchus milii Culex pipiens Drosophila melagonaster Homo sapiens Nasonia vitripennis Petromyzon marinus Schistosoma mansoni Tribolium castaneum |
Tetrahymena thermophila Toxoplasma gondii |
Arabidopsis thaliana Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Galdieria sulphuraria (Nicotiana tabacum) Solanum lycopersicum Zea mays |
Aspergillus fumigatus Aspergillus nidulans Aspergillus oryzae Aspergillus terreus Botrytis cinerea Candida albicans Candida guilliermondii Candida tropicalis Chaetomium globosum Coccidioides immitis Coprinus cinereus Cryptococcus neoformans Debaryomyces hansenii Encephalitozoon cuniculi Eremothecium gossypii Fusarium graminearum Histoplasma capsulatum Kluyveromyces lactis Laccaria bicolor Lodderomyces elongisporus Magnaporthe grisea Neurospora crassa Phanerochaete chrysosporium Pichia stipitis Rhizopus oryzae Pneumocystis jirovecii Saccharomyces cerevisiae Schizosaccharomyces pombe Ustilago maydis Verticillium longisporum Yarrowia lipolytica |
Examples of AUGUSTUS predictions can be viewed at at various genome browsers:
UCSC Genome Browser,
Wormbase: Caenorhabditis elegans, C. briggsae, C. remanei, Brugia malayi
Phytozome: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Flybase: Drosphila melanogaster
Genboree Browser: Tribolium castaneum